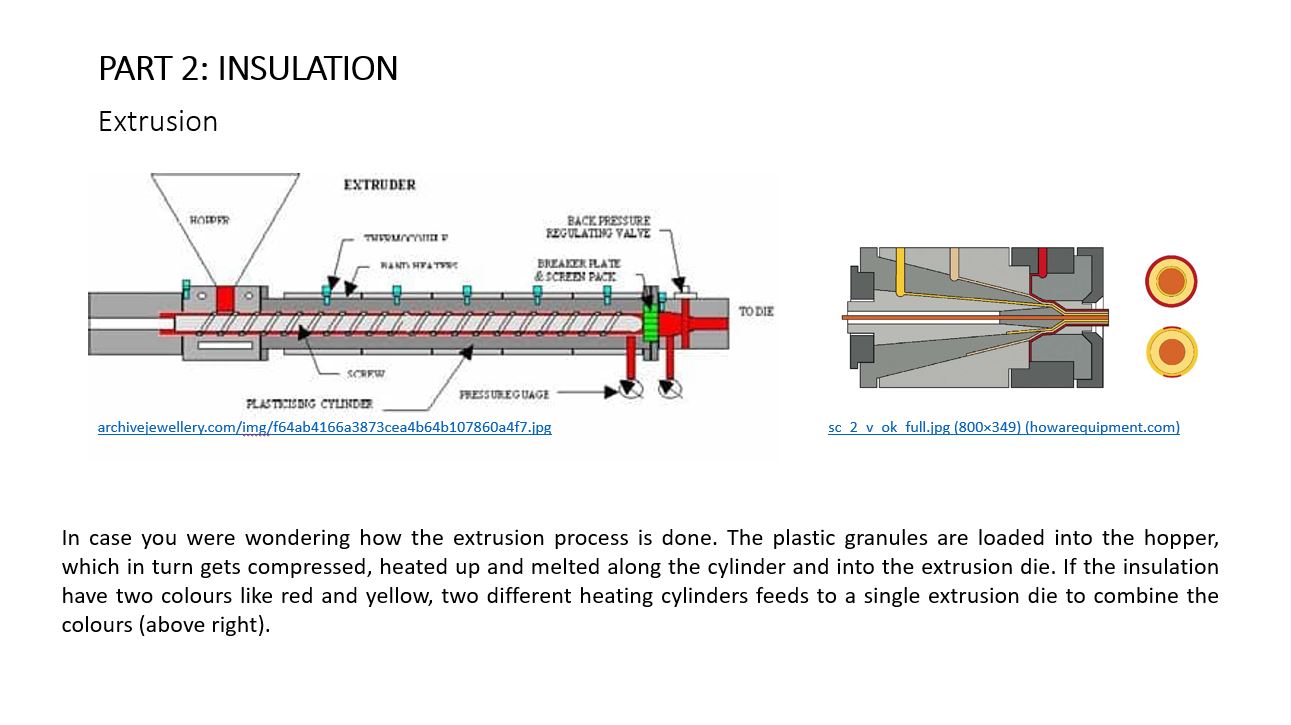
Part 2 (c) – Insulation
20,039 total views
20,039 total views

20,039 total views
20,039 total views

27 Feb 2020 | Cawangan Kejuruteraan Elektrik, JKR Pahang Product Knowledge”berkaitan kabel kuasa (Housing Wire, Medium Voltage & Low Voltage) bersama tetamu VIP Che Wan Nor Rahibiyah Binti Wan Adnan, Jurutera Elektrik Kanan. 18,194 total views
18,194 total views

18,19,20 Feb 2020 | Dewan 2020 Kangar, Perlis Pameran Sempena Kursus Kefahaman L-S1 (Rev, 4 2017) untuk kontraktor-kontraktor elektrik Negeri Perlis bersama tetamu VIP Y. Bhg. Hj. Ismail Bin Mohamad, Pengarah JKR Perlis dan Y. Bhg. Ir. Hj. Yaakob Bin Abdul Latif, Pengarah Kanan, Cawangan Kejuruteraan Elektrik JKR Malaysia. 15,610 total views
15,610 total views

We care for the environment too but we don’t use recycled plastics for our insulation materials. 21,650 total views
21,650 total views
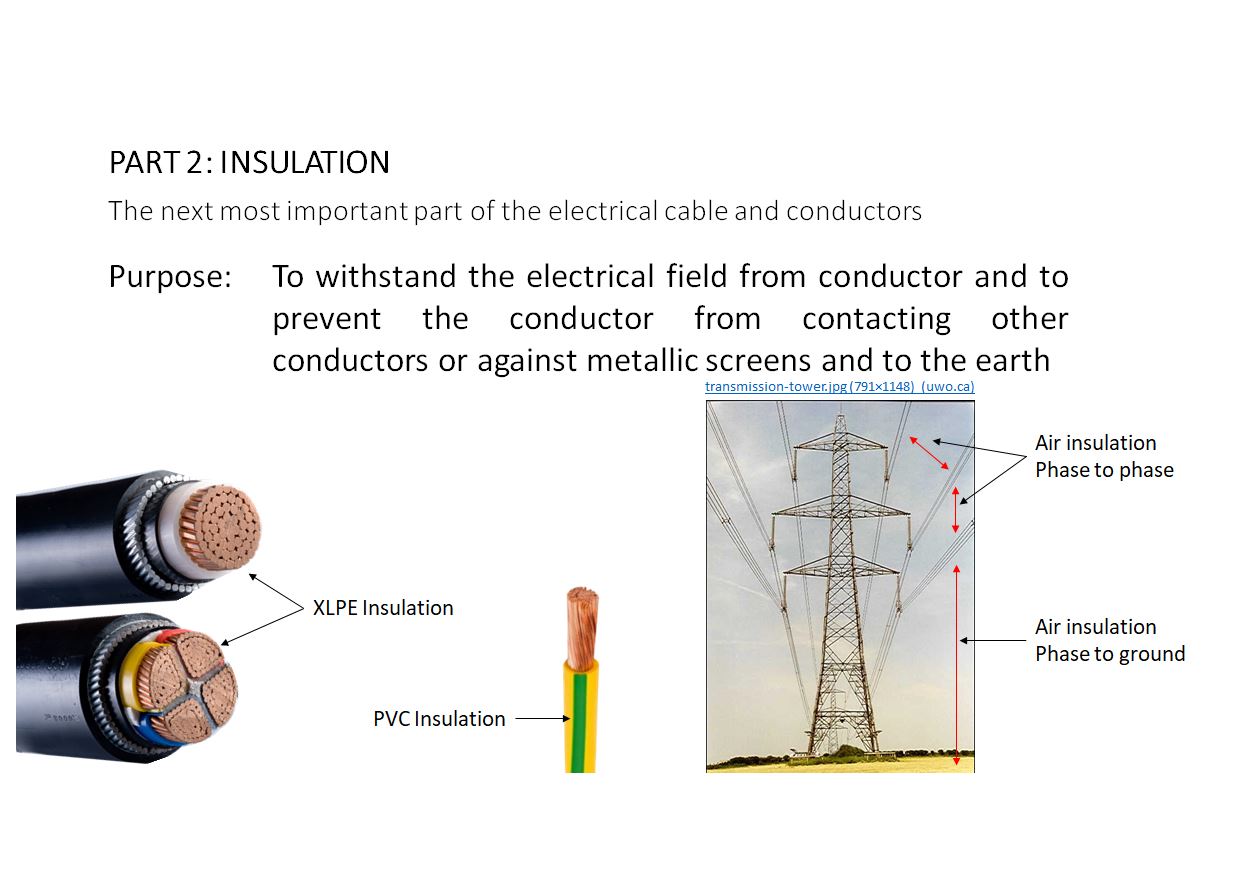
There are many types of electrical insulation in use today, with each having unique physical and chemical properties. Most common insulation materials used in electrical cables are made from plastic-polymer-based compounds. Ever wondered why bare conductors used in high voltage transmission systems do not have any insulation? The answer: air is natural insulation between phase-to-phase…
34,858 total views
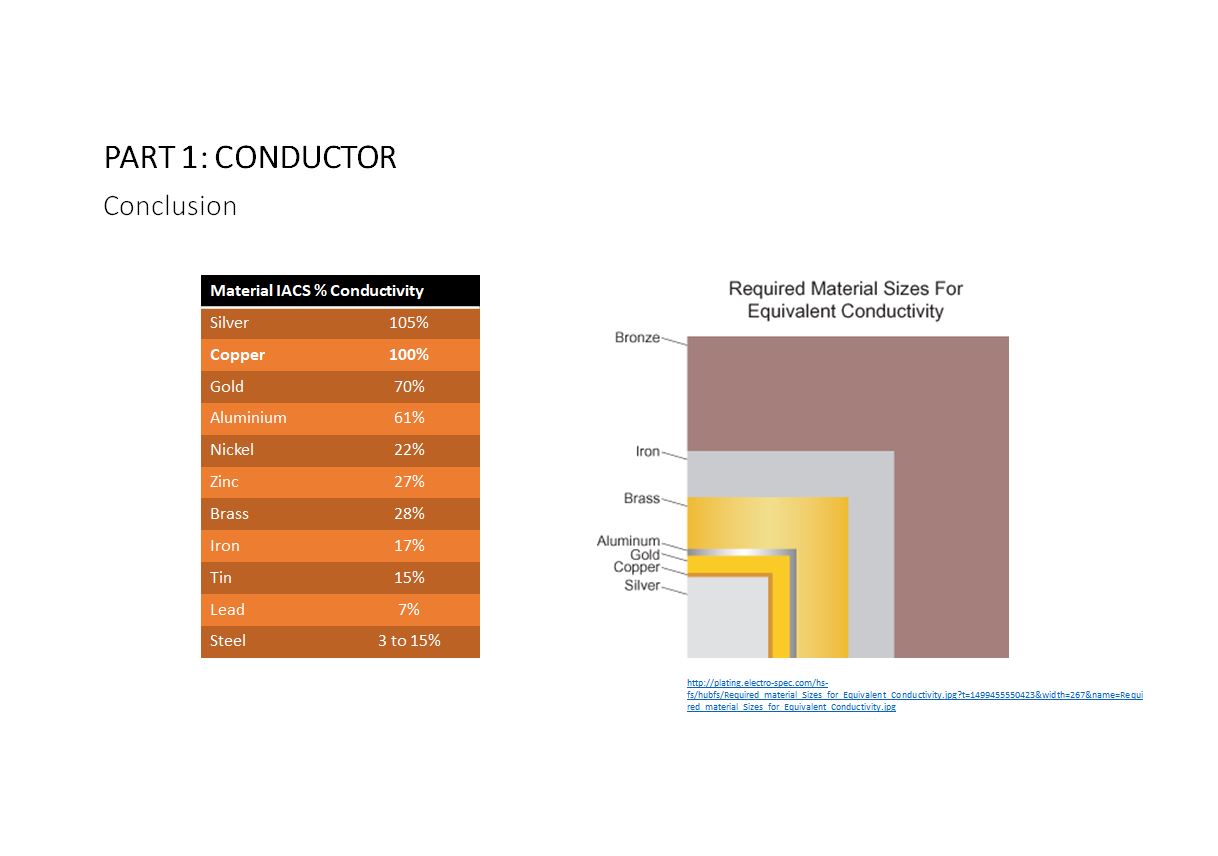
Copper and aluminium are primary choices of material for cable conductors due to its mechanical, electrical properties and of course price of the commodity itself. The table above show the comparison between various metals according to the International Annealed Copper Standard (IACS). The diagram on the right illustrates that different material due to different conductivity…
99,839 total views
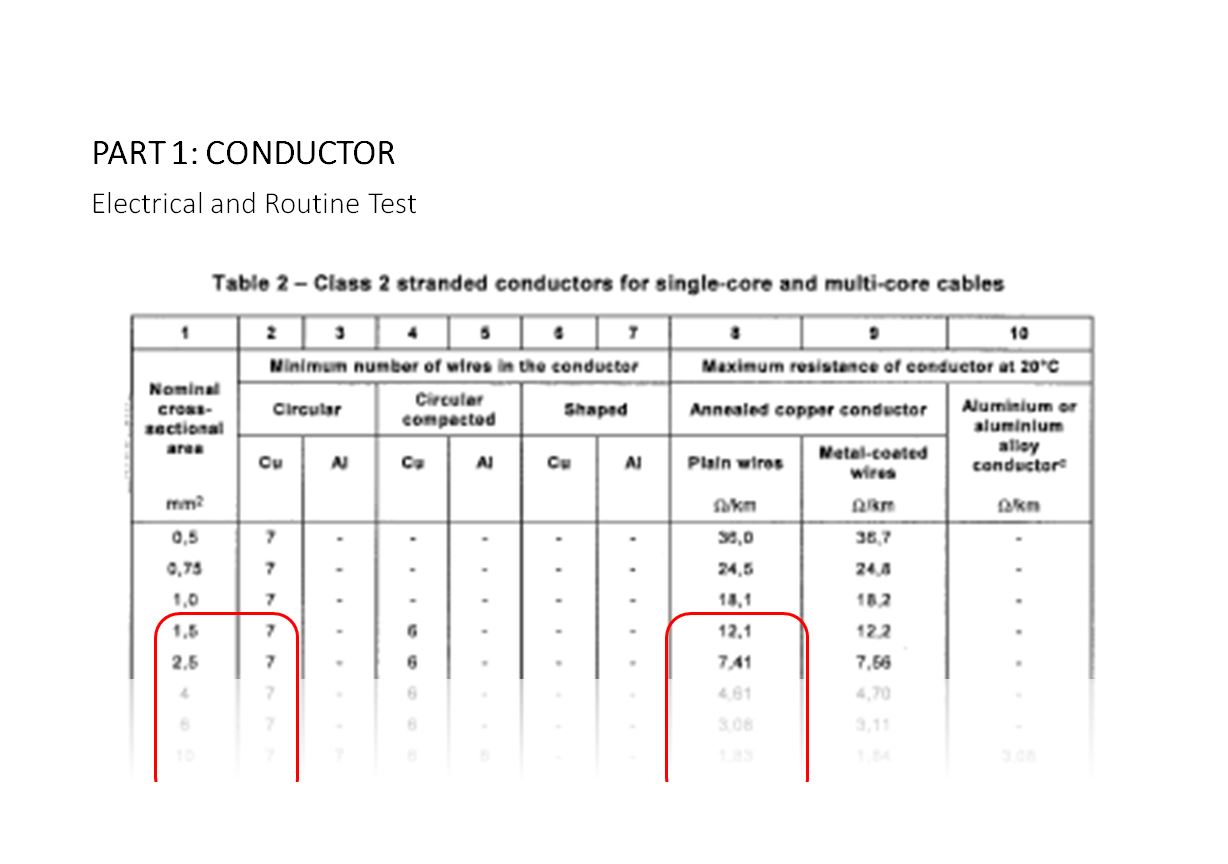
The routine test shall be tested on conductor to determine the DC resistance of the conductor at 20 oC and the measured value shall not exceed the appropriate maximum specified in table of IEC 60228 and BS 6360. This type of test is done on a 1 meter sample in a laboratory using a double…
154,215 total views
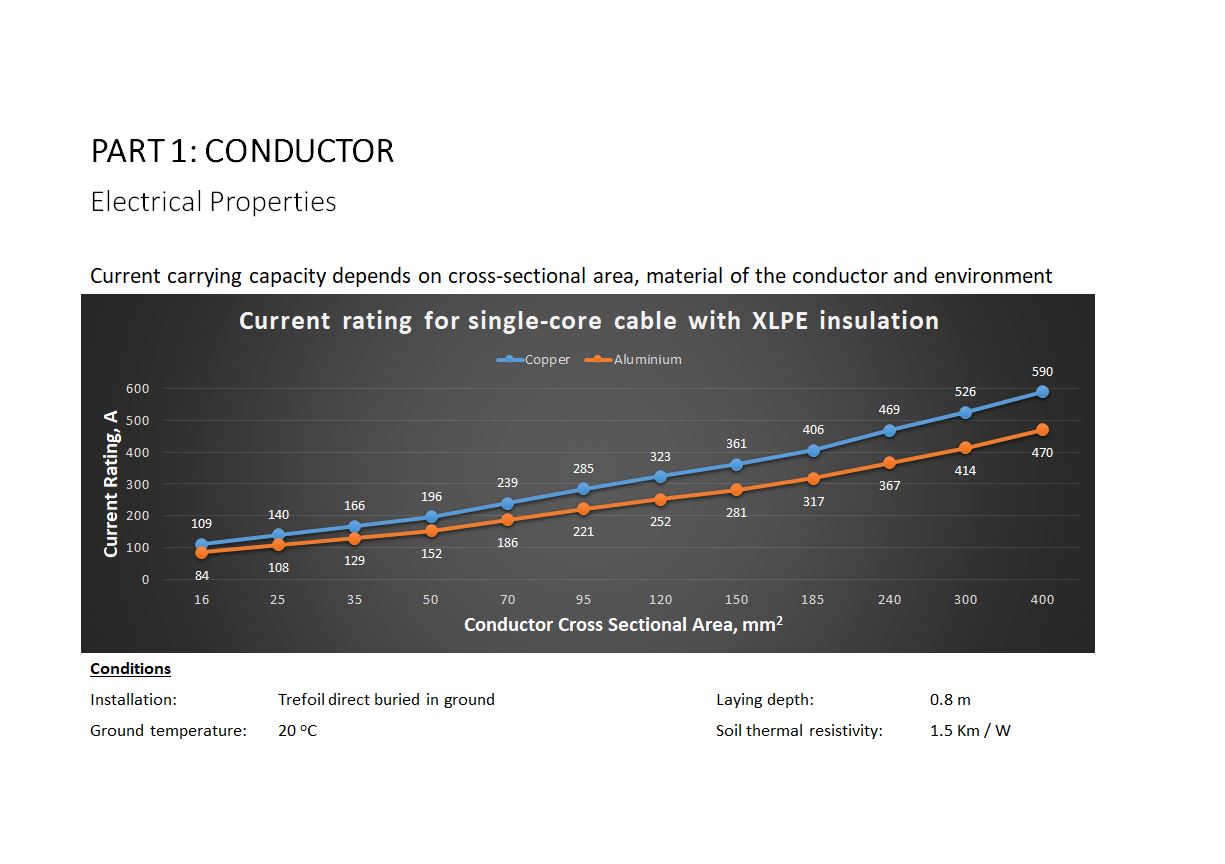
Current carrying capacity depends on the cross-sectional area of the conductor and the material it is made from. The complexity of cable routes and environmental constraints such as burial depth, type of soil will also influence the current rating. It is often referred to as “derating factor”. Therefore engineers and designers, when calculating power load…
214,088 total views
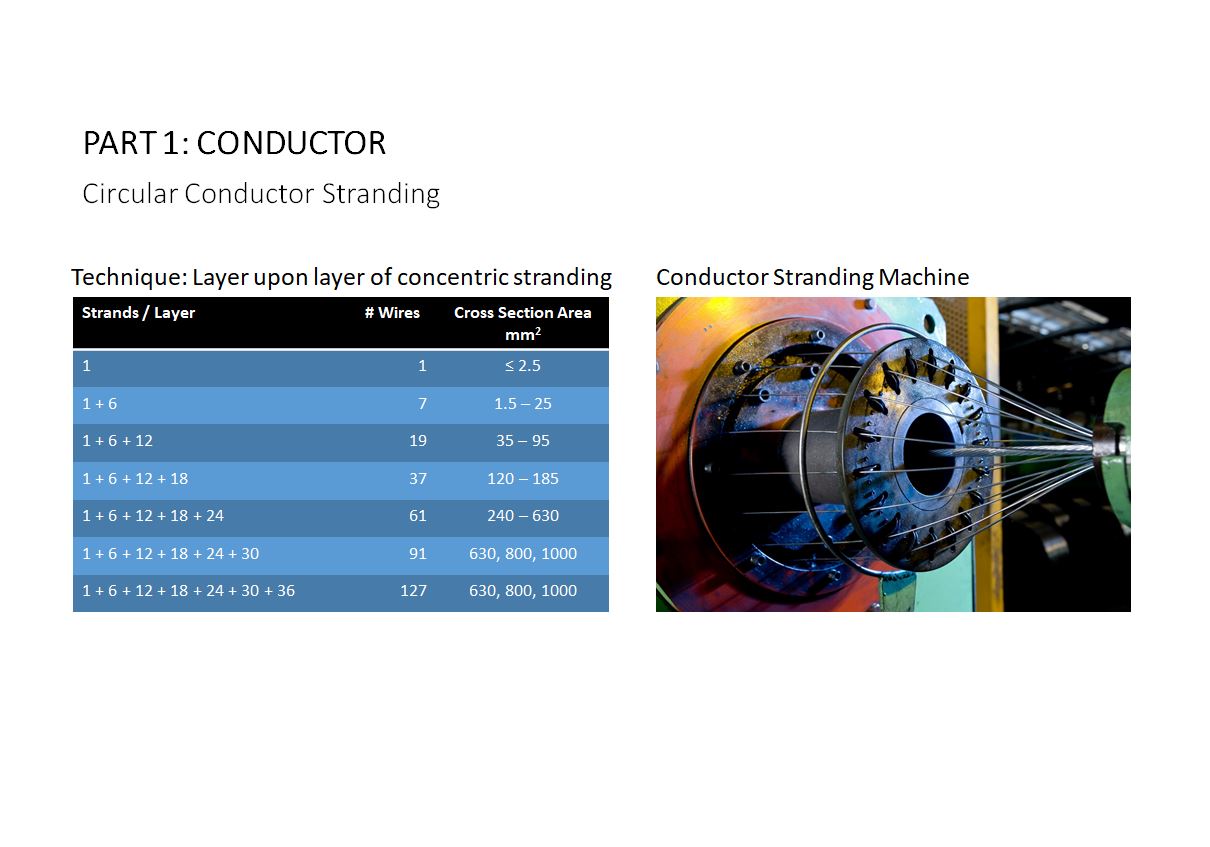
Almost any type of copper or aluminium conductor produced today undergoes concentric stranding to build up to a desired cross-sectional area. For instance it is much more practical and cost effective to produce a 19-wire 35mm2 conductor than to produce a single solid 35mm2 conductor. 108,474 total views
108,474 total views
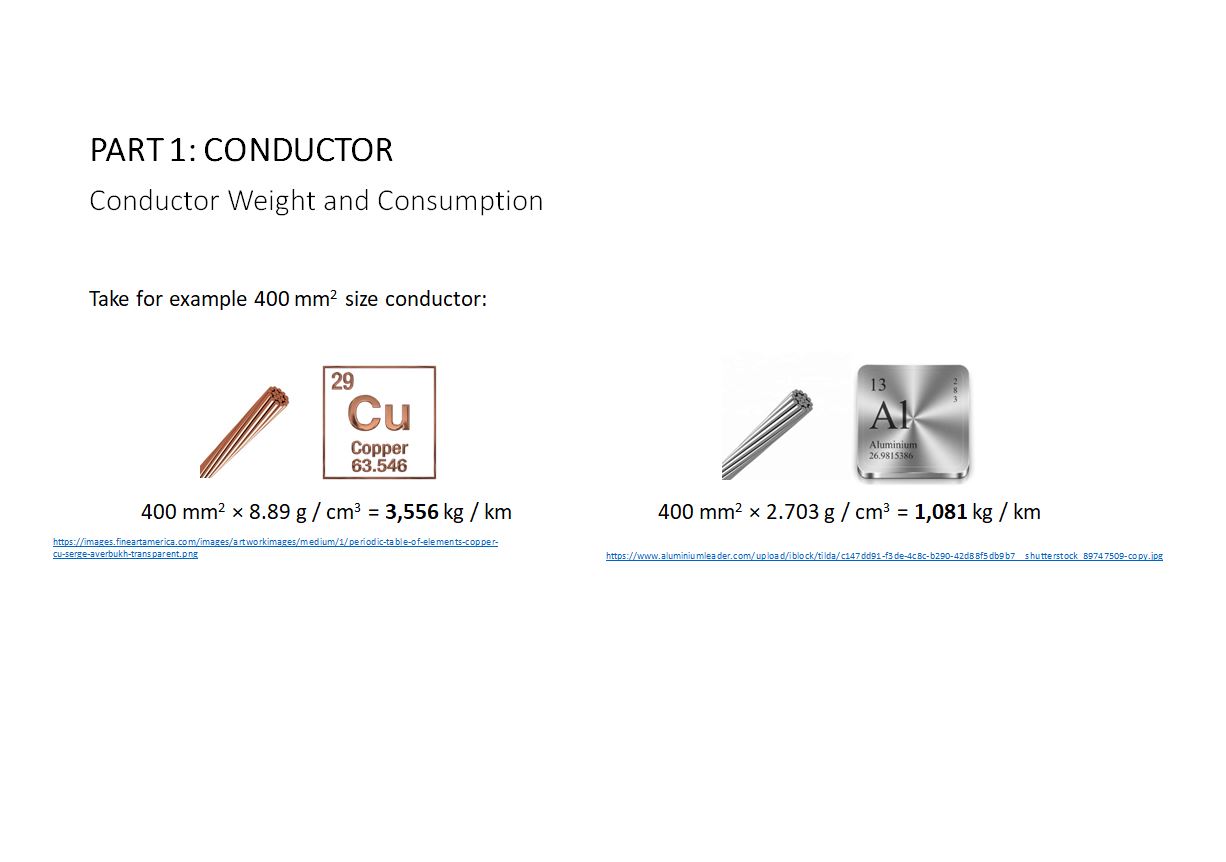
Calculating conductor weight is fairly straight forward. No complex formulas here. Simply multiply the conductor cross-sectional area by the material density of that conductor. Disclaimer: Our product knowledge sharing series is intended for information and educational purposes only. It shall not be construed as a technical guide or guarantee on our part. If you…
89,520 total views